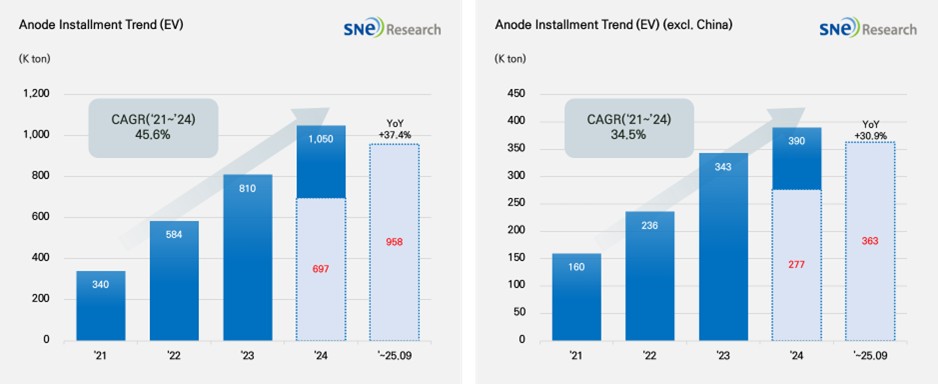
From Jan to Sep 2025, Global[1] Electric Vehicle Battery Anode Material Installment[2] Reached 958K ton, a 37.4% YoY growth
- Anode installment in the non-China market recorded 363K ton, a 30.9% YoY growth
(Source: 2025 Oct Global EV & Battery Monthly Tracker (Incl. LiB 4 Major Materials), SNE Research)
From Jan to Sep 2025, the total installment of anode materials in electric vehicles (EV, PHEV, HEV) registered worldwide was approx. 958K ton, posting a 37.4% YoY growth and staying in an upward trend. During the same period, in the global market outside China, the total installment of anode material was 363K ton, recording a 30.9% growth. Despite relatively moderate growth, the overall trend of steady growth was maintained.
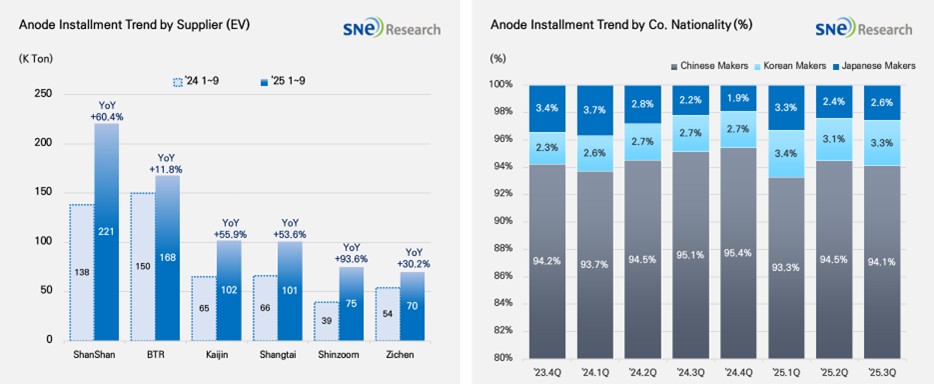
If we look at the market share held by companies, ShanShan (221K ton) and BTR (168K ton) ranked 1st and 2nd on the list, leading the global anode market. These two companies have successfully secured a stable customer base and mass production capabilities, by supplying anode materials to major battery makers such as CATL, BYD, and LG Energy Solution. Kaijin(102K ton), Shangtai(101K ton), Shinzoom(75K ton), Zichen(70K ton) were all ranked high, exhibiting a double-digit YoY growth and expanding their presence in the global market.
(Source: 2025 Oct Global EV & Battery Monthly Tracker (Incl. LiB 4 Major Materials), SNE Research)
If we look at the market shares of companies by their nationality, the Chinese anode makers accounted for more than 94% of the entire market, solidifying their absolute dominance in the market. Based on expansion of production capacity and sophistication of technology, they have been solidifying their market dominance. With the electric vehicle market expanded, more Si-anode has been adopted, leading them to further intensify cooperation with major battery makers. Although the market shares taken by the Korean anode makers were only around 3.3%, cooperation with major cell makers has been expanded to enter the market in earnest. Those efforts to cooperate with cell makers are mainly led by POSCO and Daejoo. On the other hand, the Japanese anode manufacturers accounted for only 2.6% of the market share, showing a relatively insignificant presence in the market. For example, Hitachi와 Mitsubishi maintained their conservative strategies to depend on the existing customer base, which seemed to gradually weaken their competitiveness in the market.
In 2025, the anode materials market has entered a structural inflection point, driven by both heightened supply chain risks and accelerating technological shifts. Following the U.S. preliminary anti-dumping and countervailing duty rulings on Chinese synthetic graphite, efforts to build non-Chinese supply chains have gained momentum in North America and Europe. Companies such as Vianode and Northern Graphite are expanding local synthetic graphite production to reduce dependency on China. Conversely, China began implementing export controls on synthetic graphite in November, reinforcing its market dominance and intensifying geopolitical tensions. Amid these developments, silicon–carbon composite anodes are emerging as the next-generation alternative, fueling a global race for investment and commercialization. Ultimately, future market leadership will depend on how effectively players turn external risks—such as tariffs and export restrictions—into opportunities for technological innovation and supply chain self-sufficiency. For Korean material manufacturers, this turbulent period presents a strategic window of opportunity for new market entry and differentiation.
[2] Based on batteries installed to electric vehicles registered during the relevant period.

