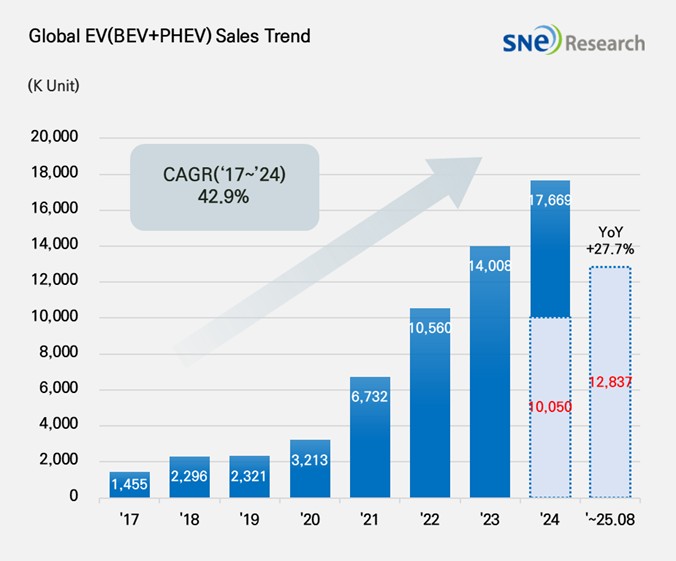
From Jan to Aug in 2025, Global[1] Electric Vehicle Deliveries[2] Recorded Approximately 12.837Mil Units, a 27.7% YoY Growth
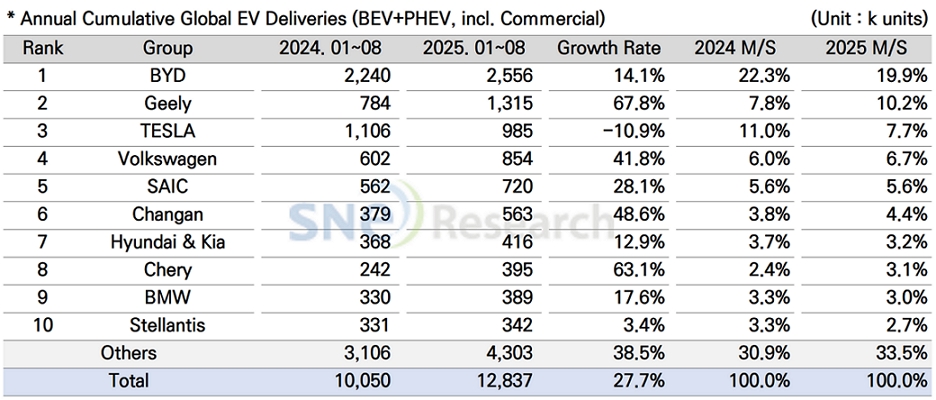
- BYD remained top by selling 2.556 mil units; Geely ranked 2nd with 67.8% growth
From Jan to Aug in 2025, the number of electric vehicles
registered in countries around the world was approximately
12.837 million units, a 27.7% increase from the same period last year (10.05
mil units).
(Source: Global EV and Battery Monthly Tracker – Sep 2025, SNE Research)
From Jan to Aug in 2025, BYD remained top in the global ranking by selling approx. 2.556 million units, recording a 14.1% YoY growth. BYD has been flexibly responding to recent changes in tariffs and subsidy policies by building production sites in the European region (Hungary and Turkey) and the Southeastern Asian region (Thailand, Indonesia, and Cambodia). While steadily increasing its brand awareness based on price competitiveness and technology, BYD has been working to diversify its model line-ups from commercial vehicles to ultra-small vehicles to improve its competitiveness across the entire ecosystem for electric vehicles. BYD has recently lowered its annual sales goal from 5.50 million units to 4.60 million units, which is equivalent to around 7% YoY growth. The major background for downward adjustment seems to be intensified competition among the Chinese OEMs in the electric vehicle market.
Geely Group in the 2nd place continued to see a double-digit growth by selling approx. 1.315 million units and posting a 67.8% YoY growth. Geely’s Star Wish(星愿) model is gaining popularity and contributing to expansion of line-ups. Its premium brand ZEEKR(极氪), hybrid-dedicated Galaxy(银河), and LYNK & CO(领克), aiming for the global market, are absorbing demands based on its multilayered brand portfolio. Geely Group has been very responsive in converting from internal combustion engine vehicles to electric vehicles. The group also accelerated the in-house development of technology for batteries, electrical equipment, and software as well as the increase of production capacities. These vertical integration and in-house technology development strategies have been evaluated as key drives behind the competitiveness of Geely. In addition, while admitting possible impacts from the US tariff policy, Geely implemented strategies to spread its production and sales bases. At the same time, it has been working on legal actions and business model adjustment in an effort to lower its dependence on local production facilities in China.
Tesla is entering a phase where it is passing through an inflection point in both demand and product cycles, leading to accumulated margin pressure from price cuts and incentives, while expanded investments in autonomous driving software are limiting the short-term earnings flexibility. This has a direct impact on the sales performance of Tesla, making it settle in the 3rd place on the list and sell approx. 985k units, a 10.9% YoY decline. By region, Tesla saw a 21.5% decline in sales in the European market (159k units), a 12.2%d decrease in the North American market (374k units), and a 6.9% decline in the Chinese market (361k units), meaning that Tesla has been going through a moderate adjustment in sales in the major markets. A slowdown in sales of Model Y and 3 has made the entire sales drop, and particularly, Model Y experienced a 11.2% decrease (716k units 636k units). Tesla’s flagship sedan Model S and SUV Model X also saw a rapid drops in sales, a 59.6% and 44.2%, respectively, meaning that Tesla may have been experiencing declining competitiveness in high-end model line-ups. On the other hand, by strengthening the automation in sales and customer service, as well as by closely combining the sophistication of FSD function and the monthly subscription-based software profit model, Tesla has been trying to restructure its mid-to-long-term profit model.
(Source: Global EV and Battery Monthly Tracker – Sep 2025, SNE Research)
Hyundai Motor Group sold approx. 416k units of electric vehicles, recording a 12.9% YoY increase and showing steady growth in the global EV market. In terms of pure electric vehicles, IONIQ 5 and EV 3 were leading the growth of sales, while small-sized, strategic models such as Casper (Inster) EV, EV, and Creta Electric received well in the market. On the other hand, some of the existing models such as EV 6, EV 9, and Kona Electric showed a slowdown in sales, failing to maintain its growth momentum. In the North American market, Hyundai Motor Group delivered 118k units, following Tesla and GM and capturing the 3rd place in the ranking. Although it saw a 14.8% YoY decrease, Hyundai outperformed Ford, Stellantis, Toyota, and Volkswagen, which adds more meanings to the sales performance. In terms of strategies, Hyundai has been focusing on localization in North America. With its Georgia plan starting operation, Hyundai’s major EV models now meet the requirements for tax credits. Changing the production site of EV 9 to North America, Hyundai lowered the price barrier to customers, enhancing their accessibility to the model. In future, Hyundai aims to establish a unwavering profit structure regardless of fluctuations in subsidies and tariffs by diversifying its electrification portfolio with the global expansion of EV 3 and introduction of EV 4 and IONIQ 9, expanding the proportion of local procurement, and also optimizing the product line-ups.
(Source: Global EV and Battery Monthly Tracker – Sep 2025, SNE Research)
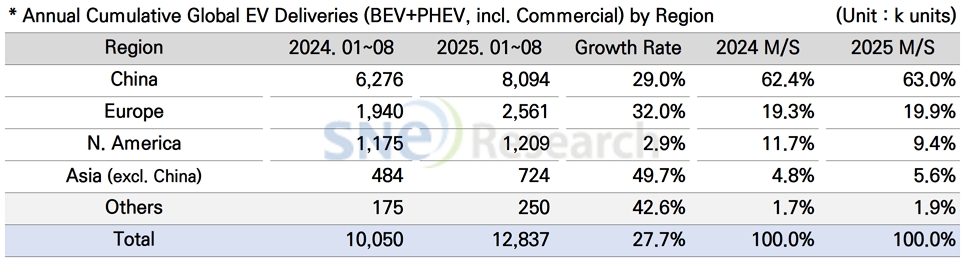
In China, taking up 62.4% of the global market share, a total of 8.094 million units of electric vehicles were sold, recording a 29.0% YoY increase. Centered around big cities in China, demand for entry-level electric vehicles expanded and the electrification of commercial vehicles increased. Autonomous subsidy policies introduced by local Chinese governments and expansion of charging infrastructure were effective in driving demand in the market. In particular, the increasing usage of LFP batteries and accelerating innovation of cost structure have led the expansion of markets for low-to-mid-priced electric vehicle models. The purchase tax exemption for new energy vehicles (NEVs) will remain in full effect until 2025 and be reduced to 50% during 2026–2027 to facilitate a gradual transition. In addition, vehicle replacement policies for older cars are stimulating replacement demand, sustaining the upward trend in NEV market penetration.
[2] Based on electric vehicles (BEV+PHEV) delivered to customers or registered during the relevant period

