<2025> Latest Status and Outlook of All-Solid-State Battery Electrolytes and Manufacturing Technologies
(In-Depth Analysis of Key Developers and Manufacturing Technologies of
Solid Electrolytes and ASSBs)
The
performance of lithium-ion batteries, which are currently the most widely used,
has continuously improved due to relentless technological advancements driven
by the surging demand for new electronic devices and electric vehicles.
Notably, energy density has dramatically increased to exceed 350Wh/kg. However,
higher energy density also entails a greater risk of fire and explosion.
Lithium-ion batteries can experience electrical failures, internal overheating,
and heat release due to mechanical damage, over-discharge, or overcharge,
potentially leading to thermal runaway and explosive reactions.
To
mitigate these risks, solid-state batteries, which incorporate solid
electrolytes, have emerged as a next-generation battery technology alternative.
The key advantages of solid-state batteries include excellent safety, high
energy density, high power output, a wide operating temperature range, and fast
charging. As a result, they offer freedom from explosion risks and can operate
safely and stably even in extreme temperatures, from sub-zero conditions to
high temperatures of 60–100°C. This enhances their applicability across a
broader range of fields.
According
to predictions by SNE Research, the global solid-state battery market size is
expected to grow to 122GWh by 2030, achieving a penetration rate of 1.6%. By
2035, it is forecasted to reach 493GWh, accounting for 6.1% of the total
battery market. Governments of countries including South Korea, the United
States, China, Japan, and various European nations are responding with
national-level support policies to secure and lead next-generation battery
technologies. In South Korea, for example, the government announced plans to
invest 117.2 billion KRW by 2028 through a program supporting three types of
next-generation batteries, including solid-state batteries, starting in the
second half of 2024.
To
prepare for the rapid shift in the paradigm of secondary batteries towards
solid-state batteries, proactive development of key materials and mass
production technologies related to solid-state batteries is essential. While
solid-state batteries have the potential to overcome the limitations of
existing batteries, several challenges remain, including ion conductivity,
interface stability, mass production technologies, and price competitiveness.
Meanwhile,
most companies predict that the commercialization of solid-state batteries will
occur around 2030. This timeline is influenced not only by the high cost of
solid electrolytes and the underdeveloped materials for commercialization, but
also by the lack of established manufacturing (production) technologies.
Therefore,
this report aims to predict the current level of manufacturing technologies
based on patents and various information, while addressing the issues related
to materials and process technologies required to manufacture solid-state
batteries. Additionally, it seeks to propose appropriate solutions to these
challenges.
Specifically,
through patent and paper analysis on solid-state batteries, the report
identifies the strengths of different countries in terms of application fields.
By analyzing the patents of major companies, it examines the manufacturing
technologies of each company. Furthermore, through a review of literature and
presentations on manufacturing technologies and methods, the report evaluates
the advantages and disadvantages of each approach and explores which
manufacturing processes are most suitable.
Strong
Points of This Report
1.
All-Solid-State Battery Technology Trends and Market Outlook
2.
Overall Issues with Solid Electrolytes and Proposed Solutions
3.
Cell Configuration and Considerations for Applying Solid Electrolytes in
Batteries
4.
Comparison of All-Solid-State Battery Cell Manufacturing Technologies and
Processes
5.
Manufacturing Technology Trends of Key Companies such as TOYOTA, HONDA, and SDI
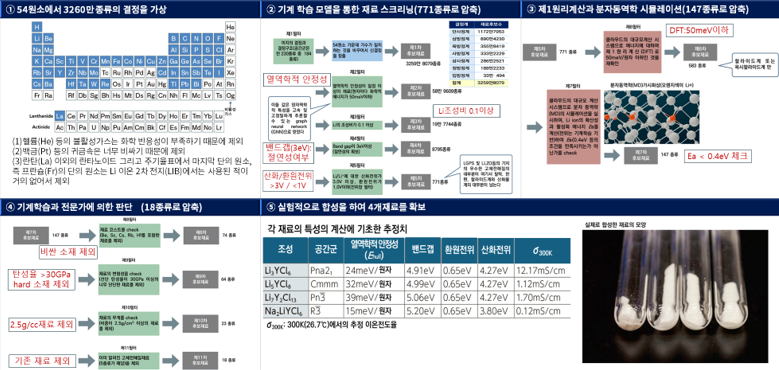
< Development of New Halide-Based Solid Electrolytes Using AI by PNNL-Microsoft >
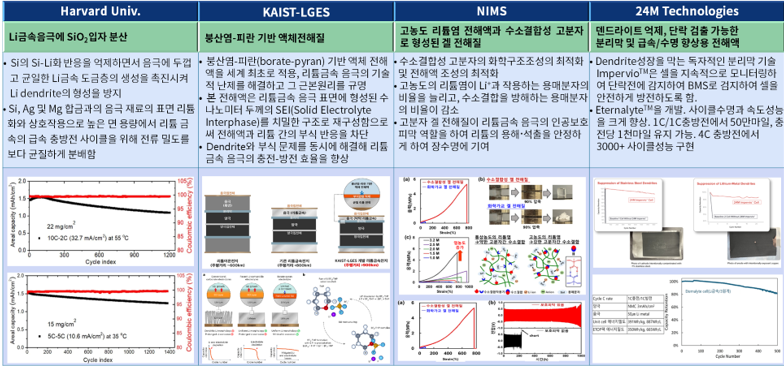
< Current Status of Technology Development for Improving the Lifespan of Li Metal Anodes >
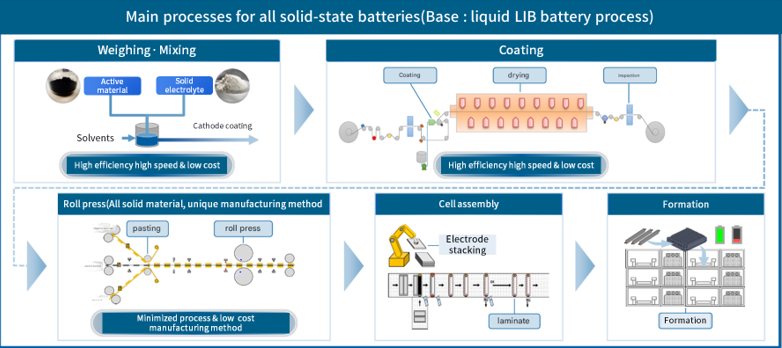
< HONDA's Solid-State Battery Manufacturing Process >
- Table of Contents -
- Overview of All-Solid-State Batteries (ASSBs)
1.1 All-Solid-State Battery (ASSB)
1.1.1 History
and Future of EV Development-------------------------------------------------------6
1.1.2 Technological Advancement and
Evolution of Batteries--------------------------------7
1.1.3 Limitations
of Lithium-Ion Secondary Batteries (LIBs) ------------------------------------9
1.1.4 Characteristics
and Necessity of ASSB Development ------------------------------------11
1.1.5 Application
Fields of ASSB ---------------------------------------------------------------------12
1.1.6 ASSB Industry Chain --------------------------------------------------------------------------24
1.1.7 Market Outlook of ASSB -------------------------------------------------------------------------25
1.1.8 ASSB
Patent Application Status ----------------------------------------------------------30
1.1.9 ASSB
Research Publication Status -------------------------------------------------------41
1.2 ASSB Technology Trends
1.2.1 Policies (projects) for
Solid-State and Next-Generation Batteries----------------------48
1.2.2 Mass
Production Status of EV Applications by Car OEMs ------------------------------51
1.2.3 Technology
Trends and Responses by Major Battery OEMs --------------------------52
1.2.4 Development and Response Status of
Material/Component Companies------------56
1.2.5 ASSB Production Status by Major OEMs-----------------------------------------------57
2. Solid Electrolytes
2.1 Solid
Electrolytes for ASSBs
2.1.1 Types and Compositions of Solid
Electrolytes---------------------------------------------60
2.1.2 Types and
Electrochemical Properties of Solid Electrolytes ----------------------------62
2.1.3 Li+ ion Conduction Mechanism in Various Solid
Electrolytes -------------------------63
2.1.4 Patent Application Trends in Solid
Electrolytes -------------------------------------------64
2.2 Oxide-Based Solid Electrolytes
2.2.1 Properties and Characteristics of
Oxide-Based Electrolytes----------------------------69
2.2.2 Ion Conductivity and Application Areas
of Oxide-Based Electrolytes-----------------70
2.2.3 Types of Oxide-Based Solid Electrolytes----------------------------------------------71
2.2.4 Advantages and Issues of Oxide-Based
Solid Electrolytes------------------------------78
2.2.5Solutions to Key Issues of Oxide-Based
Electrolytes----------------------------------79
2.3 Sulfide-Based
Solid Electrolytes
2.3.1 Characteristics of Sulfide-Based
Solid Electrolytes---------------------------------------80
2.3.2 Ion Conductivity and Applications of
Sulfide-Based Electrolytes----------------------81
2.3.3 Advantages and Disadvantages of
Sulfide-Based Solid Electrolytes----------------- 82
2.3.4 Comparison of Synthesis Methods for
Sulfide-Based Solid Electrolytes------------84
2.3.5 Structure of Sulfide-Based Solid
Electrolytes---------------------------------------------- 87
2.3.6 Overview and Characteristics of Argyrodites---------------------------------------------88
2.3.7 Overview and Characteristics of LGPS-----------------------------------------------------90
2.3.8 Overview and Characteristics of LPS----------------------------------------------------------93
2.3.9 Overview and Characteristics of Thio-LISICON--------------------------------------------95
2.3.10 Issues Related to Sulfide-Based
Solid Electrolytes--------------------------------96
2.3.11 Cost Comparison of LPSCl Using
Low-Purity Precursors------------------------------102
2.4 Halide-Based Solid Electrolytes
2.4.1 Properties of Halide-Based
Solid Electrolytes-----------------------------------------104
2.4.2 Characteristics of Halide
Electrolytes: High Li-Ion Conductivity----------------------105
2.4.3 Oxyhalide / Amorphous Structure----------------------------------------------------------106
2.4.4 Halide-Based Solid Electrolytes:
Enhancing Ion Conductivity -----------------------107
2.4.5 Development of New Solid Electrolytes Using AI
---------------------------------------109
2.4.6 Comparison with Other Solid
Electrolyte Materials--------------------------------------112
2.4.7 Oxyhalide-Based Solid Electrolytes --------------------------------------------------------113
2.4.8 Li3InCl6 Oxygen
Capture and Suppression, Safety Enhancement--------------------114
2.5 Polymer Solid Electrolytes
2.5.1 Types and Characteristics of Polymer
Matrices------------------------------------------116
2.5.2 Types and Advantages/Disadvantages of
Polymer Electrolytes----------------------117
2.5.3 Properties of Polymer Electrolytes------------------------------------------------------118
2.5.4 Issues with Polymer Electrolytes: Low
Conductivity, Stability, etc. ------------------119
2.5.5 Challenges and Solutions for Polymer
Electrolytes --------------------------------------120
2.6 Solid Electrolyte Compatibility
2.6.1 Key Considerations for ASSB Cells-----------------------------------------------------------121
2.6.2 Cathode-Electrolyte Compatibility
Issues----------------------------------------------122
2.6.3 Anode-Electrolyte Compatibility
Issues---------------------------------------------------123
2.6.4 Correlation Between Elastic Modulus
of Solid Electrolytes and Cell Performance-------------------------------------------124
2.6.5 Impact of Stack Pressure and Current
Density on Charge/Discharge----------------125
3. ASSB Electrodes
3.1 Cathode
3.1.1 Cathode Active Materials for ASSBs-------------------------------------------------------127
3.1.2 Cathode Active Material Trends---------------------------------------------------------------128
3.1.3 Development Trends of Composite
Cathodes for ASSBs-------------------------------129
3.1.4 Cathode and Composite Cathode
Processing ------------------------------------------130
3.1.5 Challenges in Composite Cathode
Development for ASSBs----------------------------133
3.1.6 Research on Surface Coating Materials
for Cathode Active Materials---------------134
3.1.7 Analysis of LPSCl-Coated NCM523
Cathode-----------------------------------------------136
3.1.8 Comparison of Electrode-Electrolyte
Interfaces with and Without Coating-------137
3.1.9 Various Cell Analyses After 50 Cycles---------------------------------------------------------138
3.1.10 Methods for Improving Cathode
Performance -------------------------------------------139
3.1.11 Recently Modified Cathode Active
Materials and Advantages------------------------140
3.2 Anode
3.2.1 Necessity of Anode Development for
ASSBs----------------------------------------------141
3.2.2 Technical Challenges in Anode Material
Development for ASSBs------------------142
3.2.3 Silicon Anode------------------------------------------------------------------------------------143
3.2.4 Si-C Anode-----------------------------------------------------------------------------------144
3.2.5 Research on Silicon-Based Anode
Materials------------------------------------------145
3.2.6 Processing of Lithium Metal and
Silicon Anodes--------------------------------------146
3.2.7 Lithium Metal Anode---------------------------------------------------------------------------148
3.2.8 Lithium Metal Anode Manufacturing
Process ---------------------------------------------149
3.2.9 Necessity of Thin Lithium Foil
Application-------------------------------------------------151
3.2.10 Research on Lithium Dendrite
Suppression and Interface Stabilization-------152
3.2.11 Development of Technologies to Extend
Lithium Metal Anode Lifespan----------154
3.2.12 Overview of Anode-Free Batteries---------------------------------------------------------155
3.2.13 Energy Density Comparison: Anode-Free
vs. Other Batteries------------------------156
3.2.14 Lithium Melt Deposition Process-----------------------------------------------------161
3.2.15 3D Grid Porous Li₄Ti₅O₁₂ Thick Electrodes-----------------------------------------------162
3.2.16 Recently Modified Anode Active
Materials and Advantages---------------------163
4. ASSB Cells
4.1 Manufacturing of ASSBs
4.1.1 Solid Electrolyte Processing------------------------------------------------------------------165
4.1.2 Cell Assembly------------------------------------------------------173
4.1.3 Cell Finishing--------------------------------------------------------175
4.1.4 Comparison of Manufacturing Processes:
ASSB vs. LIB----------------------------------176
4.1.5 ASSB Material Cost---------------------------------------------------------178
4.1.6 ASSB Cell Manufacturing Cost-------------------------------------------------------179
4.1.7 Promising ASSB Cell Concepts-------------------------------------------------------180
4.1.8 Fabrication of All-Solid-State Battery
(Semi-Solid-State Battery) Cells----------181
4.2 Oxide-Based ASSB
4.2.1 Most Promising Cell
Configurations ---------------------------------------------------------182
4.2.2 Considerations in Battery Structure----------------------------------------------------------183
4.2.3
Considerations in Battery Production------------------------------------------------------184
4.2.4
Key Performance Indicators-------------------------------------------------------------------185
4.2.5
Changes in Cell Concepts-------------------------------------------------------------------186
4.3 Sulfide-Based ASSB
4.3.1 Cell Configuration--------------------------------------------------------------------------------187
4.3.2
Considerations in Battery Structure-------------------------------------------------------188
4.3.3
Considerations in Battery Production------------------------------------------------------189
4.3.4
Key Performance Indicators--------------------------------------------------------------------190
4.3.5
Structure with Silicon Anode---------------------------------------------------------------191
4.3.6
Structural Considerations for Si/C Composite Anode Application-------------------192
4.3.7 Production Considerations for Si/C
Composite Anode Cells----------------------193
4.3.8
Key Performance Indicators for Si/C Composite Anode Application-----------------194
4.4 Polymer-Based ASSB
4.4.1 Configuration of
Polymer-Based ASSB-----------------------------------------------------195
4.4.2
Considerations in Battery Structure-------------------------------------------------------196
4.4.3 Considerations in Battery Production-----------------------------------------------------197
4.4.4 Key Performance Indicators of
Polymer-Based ASSB -----------------------------------198
4.5 Cell Energy Density
4.5.1 Assumptions for Each Material------------------------------------------------------------198
4.5.2 Gravimetric and
Volumetric Energy Density-----------------------------------------------200
4.5.3 Expected Scenarios and
Roadmap--------------------------------------------------------201
5. Manufacturing Technology of ASSBs
5.1 Lab-Scale Cell Fabrication
5.1.1 Powder Pressing Cell Fabrication-----------------------------------------------------------205
5.1.2 Three-Electrode Cell Fabrication----------------------------------------------------------207
5.1.3 Coin Cell Fabrication--------------------------------------------------------------------------208
5.1.4 ASSB by Japan NEDO -----------------------------------------------------------------------209
5.1.5 Pouch Cell Fabrication----------------------------------------------------------------------210
5.2 Cell Manufacturing
Technology
5.2.1 Advantages and Disadvantages
by Type of ASSB-----------------------------------------214
5.2.2 Manufacturing Methods by Type of Solid
Electrolyte-----------------------------------215
5.2.3 Characteristics and Pros & Cons of
the Latest Manufacturing Technologies-------216
5.2.4 Comparison of CIP, WIP, and HIP
Processes-----------------------------------------------217
5.2.5 Densification of Electrode/Electrolyte
Layers -------------------------------------------219
5.2.6 Stacking Manufacturing Technology-------------------------------------------------------220
5.2.7 Slurry/Solution Casting Manufacturing
Technology----------------------------------221
5.2.8 Extrusion Manufacturing Technology-------------------------------------------------------222
5.2.9 Tape Casting Manufacturing Technology------------------------------------------------223
5.2.10 Electrolyte Infusion Manufacturing
Technology--------------------------------------224
5.3 Manufacturing Technology for
Oxide-Based Cells
5.3.1 Sintering ------------------------------------------------------------------------------225
5.3.2 Hot Pressing -------------------------------------------------------------226
5.3.3 Spark Plasma
Sintering(SPS)----------------------------------------------------227
5.3.4 Cold Sintering Process (CSP)-------------------------------------------------------------------228
5.3.5 Microwave Sintering-------------------------------------------------------------------------230
5.3.6 Ultra-Fast High-Temperature
Sintering------------------------------------------------------231
5.3.7 Flash Sintering--------------------------------------------------------232
5.3.8 Photon Sintering and Laser Sintering--------------------------------------------------------233
5.4 Dry Processing Technology
5.4.1 Issues in Wet-Based
Electrode Manufacturing Processes-----------------------------234
5.4.2 Advantages of Introducing Dry
Processing--------------------------------------------235
5.4.3 Key Dry Coating Technologies ----------------------------------------------------------------236
5.4.4 Free-Standing Electrode
Manufacturing Technology------------------------------------237
5.4.5 Direct Calendaring Manufacturing
Technology--------------------------------------------238
5.4.6 Composite Electrode and Separator
Fabrication----------------------------------239
5.4.7 Trends in Dry Process Adoption by
Major Companies-----------------------------------240
5.4.8 Comprehensive Comparison of Dry vs.
Wet Process Technologies-------------------241
5.4.9 Patent Trends in Dry Electrode
Processing------------------------------------------------242
5.5 Cell Manufacturing Process
5.5.1 Comparison of Manufacturing
Processes: All-Solid-State vs. Lithium Metal vs. Li-Sulfur-------------------------------------------243
5.5.2 Comparison of Manufacturing Processes:
Sulfide-Based vs. Oxide-Based vs. Polymer-Based--------------------------------245
5.5.3 Cathode Manufacturing-------------------------------------------------------------------------246
5.5.4 Anode Manufacturing---------------------------------------------------------------------------252
5.5.5 Anode Foil Manufacturing Process---------------------------------------------------------256
5.5.6 Solid Electrolyte Separator
Manufacturing Process Flow-------------------------------262
5.5.7 Cell Assembly----------------------------------------------------------------------------266
5.5.8 Advantage/Disadvantage Comparison by
Manufacturing Process-------------------271
5.6 Cell Manufacturing Methods
5.6.1 Limitations of Flat Press and
Roll Press ----------------------------------------------------274
5.6.2 Difference Between HIP and Hot
Pressing -------------------------------------------------275
5.6.3 Advanced Assembly Methods for
Lithium-Based Batteries-----------------------------276
5.6.4 Comparison Between Conventional
Sintering Methods and HIP-Treated Solid Electrolytes---------------------------------------278
5.6.5 Wet Manufacturing Methods for Cathode
Materials--------------------------------280
5.6.6. Surface Coating of Cathode Active
Materials----------------------------------------------283
5.6.7 Interface Enhancement Between Cathode
and Solid Electrolyte--------------------286
5.6.8 Protective Coating Layer for Cathode-----------------------------------------------------287
5.6.9 Composite/Coating Treatment of Active
Materials---------------------------------------288
5.6.10 Methods for Improving Cell
Characteristics---------------------------------------------289
6. Trends in Manufacturing Technologies of Major Companies
6.1 TOYOTA
6.1.1 Identification of Factors
Leading to Degradation in ASSB Cells-----------------------296
6.1.2 Issues of Performance Degradation in
Long-Term Cycles------------------------------297
6.1.3 TOYOTA’s Steps for Applying ASSB-----------------------------------------------------300
6.1.4 ASSB Manufacturing: Application of Pressing--------------------------------------------301
6.1.5 ASSB Manufacturing: Application of
Sublimation Fillers-------------------------------304
6.1.6 Application of Hot Isostatic Pressing
(HIP)------------------------------------------------ -305
6.1.7 Application of Resin Packaging---------------------------------------------------------------307
6.1.8 ASSB Cell Manufacturing and Assembly
Processes---------------------------------------312
6.1.9 Solutions and Measures for Enhancing
Battery Characteristics----------------------313
6.1.10 Comparison of Materials with Other
Batteries------------------------------------------314
6.1.11 Material Change from LIB to ASSB-----------------------------------------------------------315
6.1.12 Patent Analysis of TOYOTA’s ASSB
Manufacturing Process --------------------------316
6.2 HONDA
6.2.1 ASSB Manufacturing Methods-----------------------------------------------------------------318
6.2.2 Directions for ASSB Manufacturing----------------------------------------------------------319
6.2.3 ASSB Cell Prototype Manufacturing
Process---------------------------------------------320
6.2.4 ASSB Manufacturing Process: Mixing,
Electrode Coating-------------------------------321
6.2.5 Electrode Roll Pressing/Slitting ---------------------------------------------------------------322
6.2.6 Bonding Roll Pressing, Stacking----------------------------------------------------323
6.2.7 Tab Welding, Assembly, Sealing, Aging,
Inspection--------------------------------------324
6.2.8 Comprehensive EV Valuation Structure---------------------------------------------------325
6.2.9 Battery Development Roadmap-------------------------------------------------------------326
6.2.10 Responses to Next-Generation
Batteries------------------------------------------------327
6.2.11 Advantages of HONDA's ASSB----------------------------------------------------------328
6.2.12 Differences in HONDA's ASSB Process-----------------------------------------------------329
6.2.13 Detailed Measures for Production
Technology Development----------------------331
6.2.14 ASSB P/P Line Concept-----------------------------------------------------------------333
6.2.15 HONDA's ASSB Investment Plans-----------------------------------------------------------335
6.2.16 Overview of HONDA Tochigi Sakura
Factory----------------------------------------------336
6.2.17 Entire Process of HONDA’s ASSB------------------------------------------------------------338
6.3 Nissan
6.3.1 ASSB Manufacturing
Directions-------------------------------------------------------------340
6.3.2 Identification of Factors Leading to
ASSB Performance Degradation---------------342
6.3.3 Prototype Lab Manufacturing Process ----------------------------------------------------344
6.3.4 ASSB Manufacturing Process-------------------------------------------------------------------347
6.3.5 Nissan Solid Battery P/P
Line--------------------------------------------------------349
6.3.6 Nissan’s ASSB Development Schedule-----------------------------------------------------350
6.3.7 Nissan EV 36Zero
project-------------------------------------------------------------351
6.3.8 NCM-based Cathode and Lithium Metal
Anode Batteries----------------------------352
6.3.9 Introduction of Sulfide-based Solid
Electrolyte------------------------------------------353
6.3.10 Measures to Ensure Uniform Lithium
Deposition---------------------------------------354
6.3.11 Establishment of ASSB Production Line--------------------------------------------------355
6.4 Samsung SDI
6.4.1 ASSB Cell Configuration and Mass
Production Preparation----------------------------356
6.4.2 Reduction of Vehicle Weight and
Increase in Trunk Space------------------------------357
6.4.3 Safety and Pack Weight Reduction-----------------------------------------------------------358
6.5 LG ES
6.5.1 ASSB Development Roadmap and
Application Areas------------------------------------359
6.5.2 Development of Polymer-Based ASSB-------------------------------------------------------360
6.5.3 Development of Silicon-Based Anodes
for Sulfide-Based ASSB ----------------------361
6.5.4 Development of Anode-free Electrical
Technology for ASSB---------------------------362
6.6 Hyundai Motor
6.6.1 ASSB P/P Line Operations and
Development Status-------------------------------------363
6.6.2 Battery Manufacturing Using Roll
Presses of Different Diameters------------------364
6.6.3 Dry Electrode Manufacturing Using
Binder Fiberization--------------------------------365
6.6.4 Manufacturing of Anode-free ASSB----------------------------------------------------------366
6.6.5 High-Density ASSB Manufacturing
Using WIP---------------------------------------------366
6.7 CATL
6.7.1 ASSB Development Status----------------------------------------------------------------------368
6.7.2 CATL vs. TOYOTA Strategy Comparison------------------------------------------------------369
6.7.3 High-Performance Cathode Interface
Design----------------------------------------------370
6.7.4 CATL Electrolyte Strategy-----------------------------------------------------------------------371
6.8 Solid Power
6.8.1 ASSB Structure and Development
Line-up-------------------------------------------------372
6.8.2 ASSB Manufacturing Process------------------------------------------------------------------373
6.8.3 Si Anode, Li Anode EV ASSB Roadmap ------------------------------------------------374
6.8.4 ASSB Production Roadmap -------------------------------------------------------------------375
6.9 Kanadevia(Hitachi Zosen
Corporation)--------------------------------------------------------376
6.10 Mitsui Mining & Smelting ----------------------------------------------------------------------------378
6.11 Factorial Energy-----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------379
6.12 Blue Solution
6.12.1 Blue Solutions' LMP® ASSB
Structure -------------------------------------------------380
6.12.2 Blue Solutions' LMP® ASSB (Gen
4) Characteristics ------------------------------------381
6.12.3 Blue Solutions' LMP® ASSB (Gen
4) Target Characteristics ----------------------------382
6.12.4 Extrusion Manufacturing
Process and Ah-Level Production Process for Polymer-Based ASSBs -----------------------383
6.12.5 Blue Solutions' LMP® ASSB
Manufacturing Process -----------------------------------384
6.12.6 Blue Solutions' ASSB Roadmap --------------------------------------------------385
6.13 QuantumScape
6.13.1 QS ASSB Manufacturing Process
and Cell Characteristics-----------------------------386
6.13.2 QS ASSB Cell Specifications
and Performance-------------------------------------------387
6.13.3 QS ASSB Performance and
Roadmap-----------------------------------------------------388
6.13.4 Solid Electrolyte Separator
Production Technology: Cobra--------------------------389
6.13.5 Applied Product QSE-5 B ASSB-------------------------------------------------------------390
6.13.6 Introduction of Advanced
Production Equipment: Raptor----------------------------391
6.14 SES AI
6.14.1 SES Complete Cell Structure------------------------------------------------------------------392
6.14.2 SES Cell Performance and 103Ah
Cell Safety Test---------------------------------------393
6.14.3 SES Cell P/P Line Key Processes-------------------------------------------------------------394
6.15 ProLogium
6.15.1 ProLogium ASSB Cell
Structure-------------------------------------------------------------395
6.15.2 Ceramic Separator: CSE (Composite Solid Electrolyte –
Oxide + Solid Polymer Electrolyte)---------------396
6.15.3 ProLogium ASSB Line
Configuration and Trends-------------------------------------398
6.15.4 ProLogium ASSB Key
Manufacturing Processes-----------------------------------------399
6.16 Johnson Energy Storage
6.16.1 Cell Information and
Related Characteristics--------------------------------------------400
6.16.2 Slurry Coating Process--------------------------------------------------------------------401
6.16.3 Co-Extrusion Process----------------------------------------------------------------------403
6.17 TaiyoYuden(太陽誘電)
6.17.1 MLCC Type ASSB Structure---------------------------------------------------------405
6.17.2 MLCC Type ASSB Manufacturing Process------------------------------------------------406
6.18 TDK--------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------410
6.19 TDL--------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------411
6.20 Nippon Electric Glass (NEG)-------------------- -----------------------------------------------------413
6.21 Sevenking Energy-------------------------------------------------------------------------------------414
6.22 Solivis
6.22.1 Company Overview, Performance,
and Notable Information--------------------415
6.22.2 Solivis Solid Electrolyte Development----------------------------------------------------416
6.22.3 Sulfide-Based Solid
Electrolyte Hengsheng 1st Factory Groundbreaking---------417
6.22.4 Solivis Solid Electrolyte
Product Line: SICON Series 3 Types------------------------418
6.23 NANBOCAMP
6.23.1 NANOCAMP History---------------------------------------------------------------------------419
6.23.2 Argyrodite Oxysulfide Solid
Electrolyte Development-----------------------------420
6.23.3 Manufacturing Process
Establishment and Characterization-------------------------421
6.23.4 Cell Evaluation System
(Evaluation System from Raw Materials to Cells)-------- -422
6.23.5 Plant Completion, Facility
Expansion and Construction-------------------------------423
6.23.6 Production Capacity, Revenue,
and Customer Order Supply-------------------------424
6.24 ENFLOW
6.24.1 Enflow History and Plant
Status-------------------------------------------------------------425
6.24.2 Spray Pyrolysis Process and Spherical
Fine Powder Production Method-------426
6.24.3 Scale-Up Plan and Commercialization----------------------------------------------427
6.25 Umicore
6.25.1 Umicore’s Roadmap for
Cathode materials ----------------------------------------------428
6.25.2 Umicore’s All-Solid-State Cathode
Active Material IP Portfolio-----------------------429
6.25.3 Umicore’s Battery Development
Progress---------------------------------------------430
6.25.4 Breakthrough in ASSBs through
Catholyte------------------------------------------------431
6.26 Panasonic----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------432
6.27 Lotte Energy Materials-----------------------------------------------------------------------------433
6.28 Idemitsu-----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------434

