[2023] Lithium-ion Battery Electrolyte Technology Trends and Market Forecast (~2030)
Recently, the secondary battery market has
expanded from small IT applications to ESS and electric vehicles. Japanese companies such as Panasonic, which
developed secondary batteries and pioneered the industry, are losing out to
Korean powerhouses such as LGES, while Chinese companies such as CATL, BYD, and
CALB are further expanding their M/S with the support of the Chinese government
and an unlimited domestic market. Although the Korean, Chinese, and Japanese
"trilateral system" is expected to continue for the foreseeable
future, North America and Europe are also showing continued interest in the
large-capacity secondary battery manufacturing and materials market due to the
expansion of the electric vehicle market. In particular, the policies and
regulations of each country, such as the IRA, are expected to significantly
change the landscape of the secondary battery market.
The electrolyte is mainly composed of
solvents, lithium salts, and additives. Depending on the nature of the product,
the electrolyte will be developed in collaboration with lithium-ion secondary
battery manufacturers. For small IT-type products, the development period is as
short as three to four months, while electrolytes for xEVs are developed and
evaluated for more than a year. Excellent R&D capabilities are required to
develop and respond to various products according to customer needs.
In the past, the electrolyte market was dominated by Japan and South Korea, but with the recent rapid growth of Chinese companies, the top three market shares have been taken over by Chinese companies. In Korea, Donghwa Electrolyte, Soulbrain, and Enchem have been able to grow together as electrolyte suppliers with the three major lithium-ion secondary battery companies (Samsung SDI, LG Energy Solution, and SK energy). In Japan, Mitsubishi Chemical has diversified its portfolio of customers producing IT small, xEV medium and large cells. In China, Tinci, Guotai-Huarong, and Capchem dominate the market.
Lithium salts (LiPF6), the main
ingredient of electrolyte, have been mostly supplied by Japanese companies in
the past, but the game has changed as Chinese companies have increased their
CAPA. In South Korea, Foosung provides general-purpose lithium salts (LiPF6),
while Chunbo mass-produces specialized lithium salts (LiFSI, LiPO2F2,
LiDFOP, LiBOB). Additives are added during the electrolyte manufacturing
process to improve the lifespan and stability of Li-ion secondary batteries,
such as SEI protection, overcharge prevention agents, and conductive
properties. While Japanese companies dominate the additives market, in Korea
Chunbo and Chemtros are among the main suppliers.
Electrolyte is one of the four key materials that make up a secondary battery. In the manufacturing cost composition of a typical Li-ion battery, the order of importance is anode material > separator > cathode material > electrolyte. To increase the energy density per unit cell, secondary battery manufacturers are increasing the input of anode and cathode materials, while reducing the input of electrolyte. However, from 2022 to 2030, the battery market is expected to grow at an average annual rate of around 23% (by capacity). The electrolyte market is expected to grow accordingly.
For large-scale rechargeable batteries for electric vehicles and ESS, the amount of electrolyte used is about 200 times to 4,000 times higher on a unit cell basis than for IT, so securing stability is becoming a particularly important issue. In addition to liquid electrolytes and gel polymer electrolytes (polymers) that are currently commercialized, research and development is underway to improve the stability of solid polymer electrolytes and all-solid ceramic electrolytes with excellent high temperature stability.
This report provides detailed technical
information on finished electrolyte products and their components for
application in lithium-ion secondary batteries and forecasts the demand and
market for binders based on our various forecasts to help readers understand
the overall scale.
Finally, by summarizing the electrolyte demand of major battery manufacturers and the supply status and outlook of electrolyte companies, the report aims to provide researchers and interested parties in this field with a wide range of insights from technology to market.
Strong points of this report
1. overall overview and technical information
on electrolyte finished products and components
2. Introduction to solid and polymer
electrolytes that will be applied to next-generation batteries other than
conventional LIBs
3. Provides objective data on the electrolyte
market outlook based on our forecast data
4. Detailed information on the product and
production status of major electrolyte players in Korea, China, and Japan
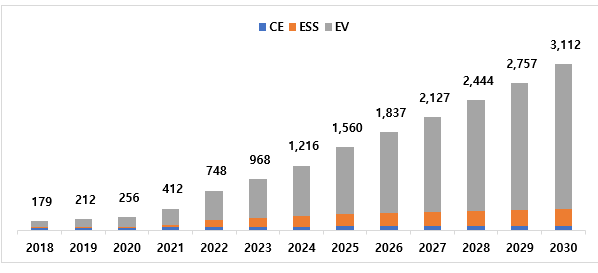
< Global
Electrolytes Market Demand Forecas (~2030)>
* Based on SNE battery
demand forecasts
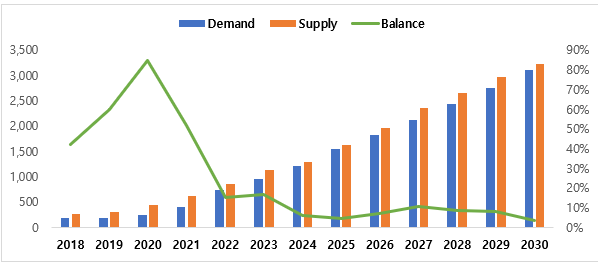
< Global Electrolyte Supply and Demand Outlook (2018~2030)>
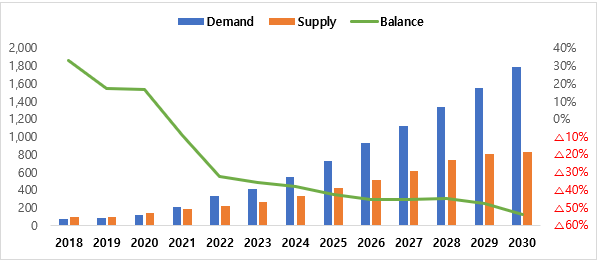
< Electrolyte Supply and Demand
Outlook for Non-Chinese Markets (2018~2030)>
* Except
for Chinese market supply and demand
[Index]
Outline of Report 7
Chapter Ⅰ. Electrolyte Overview
1.1 Understanding of electrolytes 10
1.2 Development trends and major
issues of electrolytes 13
Chapter Ⅱ. Development Trend of Liquid Electrolytes
2.1 Composition of liquid
electrolytes 35
2.2 Characteristics of liquid
electrolytes 56
2.3 Flame retardant material 72
Chapter Ⅲ. Development Trend of Polymer Electrolyte
3.1 Types of polymer electrolytes
101
3.2 Characteristics of polymer
electrolytes 113
3.3 Manufacturing method of
polymer electrolytes 121
Chapter Ⅳ. Solid Electrolytes
4.1 Necessity for development of
solid electrolytes 130
4.2 Types and technical
characteristics of solid electrolytes 133
4.3 Development trends of solid
electrolytes 135
Chapter Ⅴ. Latest Development Trends of Electrolytes
5.1 High voltage electrolyte
solvents 152
5.2 Lithium salts 159
5.3 Additives 173
5.4 Polyelectrolytes 200
Chapter Ⅵ. Electrolyte Solvents
6.1 Cyclic carbonate 205
6.2 Linear carbonate 209
6.3 Gas generation mechanism
by additives for forming the protective film on the electrode surface 216
Chapter Ⅶ. Electrolyte Additives
7.1 Electrolyte additives
for high-Ni cathode interface stabilization 226
7.2 Electrolyte additives
for improved output characteristics 232
7.3 Electrolytes using LiFSI
salts 235
7.4 Flame retardant additives
for improved thermal stability 237
7.5 Additives for
high-capacity anode interface stabilization 238
Chapter Ⅷ-1. Electrolyte Market Trends and
Outlook
8.1.1 Electrolyte demand by
country 240
8.1.2 Electrolyte usage by
application 242
8.1.3 Market status by
suppliers 244
8.1.4 Electrolyte demand by
LIB companies 252
(SDI/LGES/SKon/Panasonic/CATL/ATL/BYD/Lishen/Guoxuan(Gotion)/AESC)
8.1.5 Electrolyte demand
outlook 317
8.1.6 Electrolyte CAPA and
supply & demand outlook 318
8.1.7 Electrolyte price
trends 320
8.1.8 Electrolyte market
size forecast 324
Chapter Ⅷ-2. Electrolyte
Material Status
8.2.1 General lithium salts (LiPF6)
325
8.2.2 Non-LiPF6 lithium
salts 326
8.2.3 Functional additives 328
Chapter Ⅸ. Electrolyte Manufacturer Status
9.1 Korean electrolyte
companies 330
Dongwha Electrolyte /
Soulbrain / Enchem / Foosung / Chunbo / Chemtros
9.2 Japanese electrolyte
companies 375
Mitsubishi / Ube /
Centralglass / Tomiyama / MUIS / Nippon Shokubai
9.3 Chines electrolyte
companies 412
Tinci / Capchem / Guotai Huarong / Shanshan / Jinniu / DFD / Shinghwa

